21+ Composite Functions
Composite Functions. (a) (f ∘ g) ( x) (b) (f ∘ g) (2) (c) g (f (x)) (a) write d as a function of n. It is also sometimes necessary to carry out the reverse process, decomposing a complicated function into two or more simple functions.

(b) write s as a function of d. When you have just one function on its own, say f (x) = x 2 + 2. Practice working with example problems to master compositions of two, three, and more functions, as well as.
couverture escalier exterieur couleur marron glace voiture cuisine rose gold cointra supra compact manual
Chapter 3. Polynomial and Rational Functions. 3.4 Zeros of
F ( x) = 2 x + 1, g ( x) = x + 5. (a) (f ∘ g) ( x) (b) (f ∘ g) (2) (c) g (f (x)) (a) write d as a function of n. For the functions f (x) and g (x), when g (x) is used as the input of f (x), the composite function is written as: So, \ (f (2) = 3 (2) + 2 = 8) and.

3.3 derivatives of composite functions: Composite functions anwser key displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept. Learn more about composition of functions here. Therefore, we are mapping onto. In this lesson, i will go over eight (8) worked examples to illustrate the process involved in function composition.

Composite functions anwser key displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept. A composite function of two functions combines the. A composite function is a function created when one function is used as the input value for another function. A function made of other functions, where the output of one is the input to the other. 3.3 derivatives of composite.

Find g o f ( x) 4. A function made of other functions, where the output of one is the input to the other. If we are given two functions, it is possible to create or generate a “new” function by composing one into the other. Find g o f ( x), also evaluate at x = 2. The composite.

Learn more about composition of functions here. A composite function of two functions combines the. Find f o g ( x), also evaluate at x = 2. 3.3 derivatives of composite functions: Sometimes if you create a composite function you need to consider the domain of the new function.

( gof) (x) = g ( f (x) ) similarly, ( f og) (x) = f (g (x)) so, to find (gof) (x), take f (x) as argument for the function g. (a) (f ∘ g) ( x) (b) (f ∘ g) (2) (c) g (f (x)) (a) write d as a function of n. Composite functions are the result.

For the functions f (x) and g (x), when g (x) is used as the input of f (x), the composite function is written as: The chain rule1 3.3 derivatives of composite functions: Essentially, the output of the inner function (the function used as the input value) becomes the input of the outer function (the resulting value). Find f o.

Find g o f ( x), also evaluate at x = 2. A function made of other functions, where the output of one is the input to the other. This video defines a composite function and shows how to determine the value of a composite function and how to determine a composite function given two func. Inverse functions undo each.

The chain rule in this section we want to nd the derivative of a composite function f(g(x)) where f(x) and g(x) are two di erentiable functions. This page will show a variety of composition of functions examples. Composite functions are the result you get when you apply one function to another. Find g o f ( x), also evaluate at.
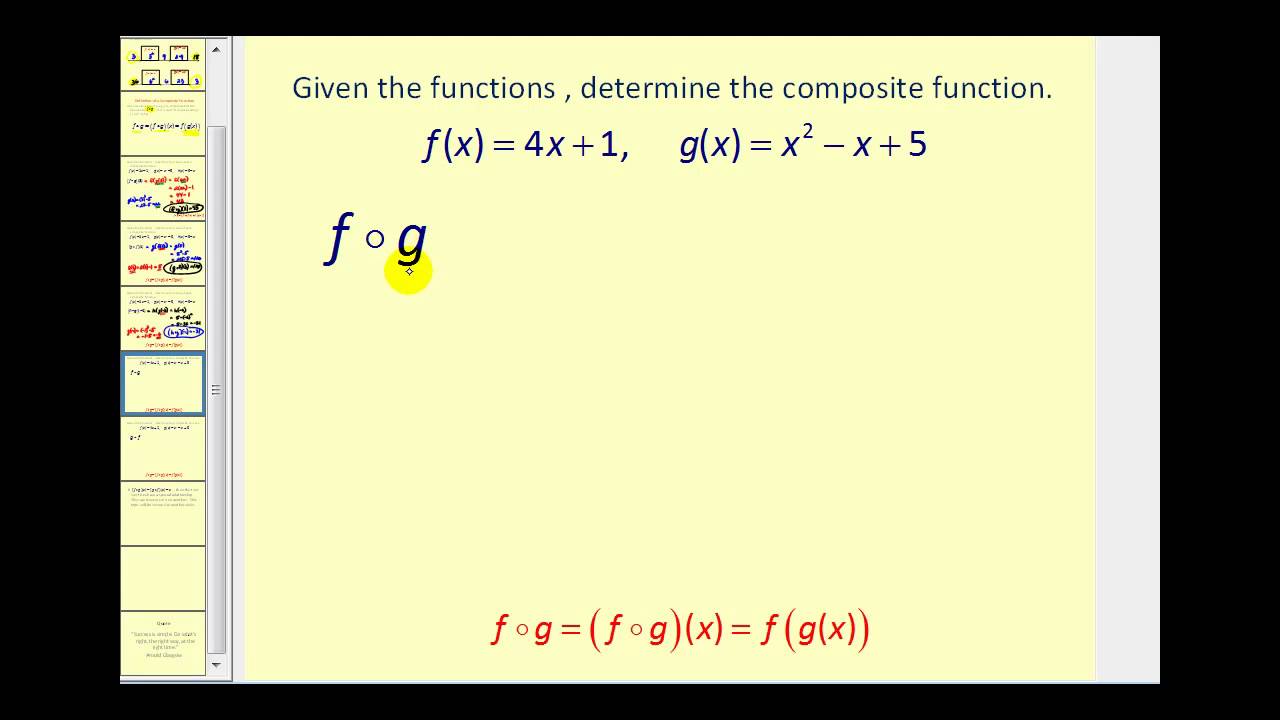
Composite functions anwser key displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept. In this lesson, i will go over eight (8) worked examples to illustrate the process involved in function composition. Inverse functions undo each other when we compose them. Practice working with example problems to master compositions of two, three, and more functions, as well as. Often the domain.