31++ Conservation Of Momentum Equation Inelastic Collision
Conservation Of Momentum Equation Inelastic Collision. Ask students to give examples of elastic and inelastic collisions. An inelastic collision is any collision between objects in which some energy is lost.

In a perfectly inelastic collision, two Box 1 moves with speed v1 and collides with box 2 that is initially at rest. Momentum is crucial to our understanding of atomic and subatomic particles because much of what we know about these particles comes from collision.
corniere angle mur coiffure coupe carre court degrade coiffure cheveux court afro femme coiffure homme 2019 degrade avec trait
8.6 Collisions of Point Masses in Two Dimensions BCIT
The inelastic collision formula is articulated as. Momentum is conserved, but internal kinetic energy is not conserved. First, for an inelastic collision, it was measured the length and mass of the two carts. M 1 v 1 = m 1 + m 2 v ′.
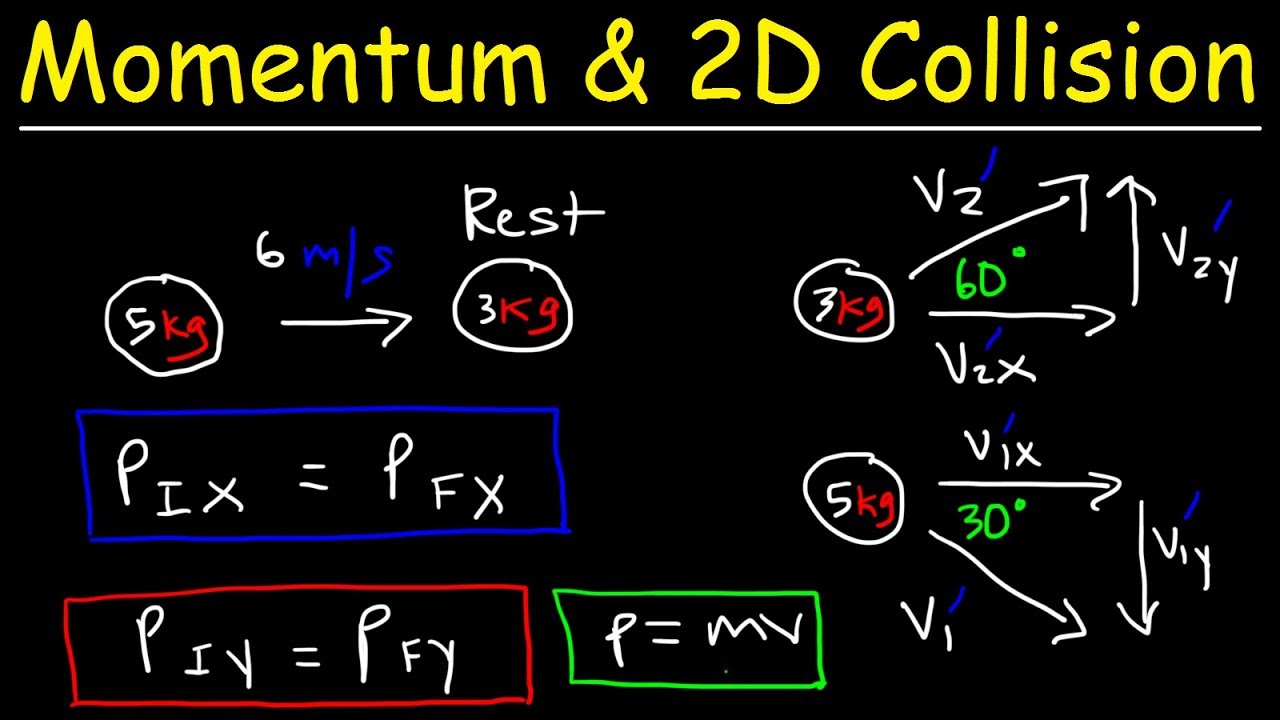
A special case of this is sometimes called the perfectly inelastic collision. M 1 u 1 + m 2 u 2 = m 1 v 1 + m 2 v 2. That is, the total initial momentum of the system p~i is equal to the total final momentum p~f: Another approach is to combine elastic and inelastic collisions equations into.

Thus, the conservation of momentum equation simplifies to m 1 v 1 = m 1 + m 2 v ′. Let the coefficient of restitution of the colliding bodies be e. Where mass of body 1 = m 1. Momentum is conserved, m1→v i1 + m2→v i2 = m1→v f1 + m2→v f2 = (m1 + m2)→v f m 1.

Since v 2 = 0 and v' 1 = v' 2 the above solved for the velocities after the collision becomes; Ask students to give examples of elastic and inelastic collisions. First, for an inelastic collision, it was measured the length and mass of the two carts. Another approach is to combine elastic and inelastic collisions equations into one equation.

Kinetic energy is only a part of the entire energy. Where mass of body 1 = m 1. That is, the total initial momentum of the system p~i is equal to the total final momentum p~f: In an inelastic collision momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not. Then, applying newton’s experimental law and the law of conservation of momentum,.